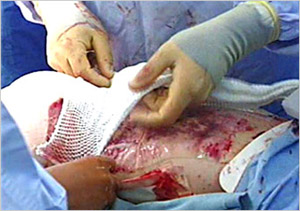

- Fixation and compression are of significant
importance. Elastic bandages, padded "tie-over"
dressings, vacuum devices, splints and other methods,
depending on circumstances, should be used to ensure
the material adheres to the wound without shear, and
that hematomas and seromas do not accumulate.

- Inspect for hematoma and seroma formation
upon dressing changes

- Elastic net dressing can be
attached by staples or other suitable methods. It will
be left in
place until the silicone is removed and offers the following
advantages:
- Helps prevent dislodgement
- Keep INTEGRA™
Bilayer Matrix Wound Dressing in intimate contact
with the wound bed
- Easy to see
through for observing Neodermis
- When applied correctly, the expanded
interstices will be open about 1-2 cm and the silicone
will have slight indentations from the elastic net dressing

- Apply non-adherent absorbent dressings
as the inner dressing layer

- Use topical antimicrobials
such as silver impregnated dressings to help maintain
a bacterial
barrier over INTEGRA™ Bilayer Matrix Wound Dressing


Outer Dressings
Note:
Do not let Dakins Solution, petroleum-based
products, e.g., Xeroform, or enzymatic debridement agents,
(e.g., Collagenase), come in contact with the INTEGRA™
Bilayer Matrix Wound Dressing application sites.
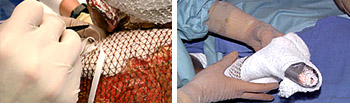
Use splints or bolsters, per unit protocols, during first
5-7 days. Splints should be applied and should stay on
at all times (except when performing wound care).
The VAC (Vacuum Assisted Closure)* may be used over unmeshed
or meshed INTEGRA™ Bilayer Matrix Wound Dressing
sites, in particular, as a bolster dressing for difficult
anatomical sites or wound beds, such as the axilla.
*VAC is a registered trademark of Kinetic Concepts, Inc.
(KCI)